Early in 2006, I wrote an article for Low End Mac entitled VNC, Basilisk II, and SheepShaver: 3 Ways to Run Classic on an Intel Mac. In it, I noted that the then-new Intel-powered Macs were unable to run older Mac software in called Classic Mode, but that there were at least a couple of ways to get around that, including Basilisk II, which emulates old 680×0 Macs, and SheepShaver, which emulates newer pre-OS X PowerPC Macs.
While SheepShaver, promising emulation of Macs from the late 1990s, would seem a better solution than Basilisk – emulating Macs from the 1980s through early 1990s – I noted in that article: “I’ve been trying to make (SheepShaver) work . . . So far, all I get is a black window.”
While many of us no longer rely on old Classic mode software, Apple gives Classic mode even less support than at the time I wrote that article. At that time, if you had a PowerPC Mac, you could still run older software in Classic Mode if needed. But now, if you’ve upgraded to Mac OS X 10.5 Leopard, your PowerPC Mac will also be Classic-less.
I recently bought a secondhand 12″ G4 PowerBook (more on that another time); it came with Mac OS X 10.4 installed, but I upgraded it to 10.5, thus nuking its Classic Mode capabilities. So I thought it might be time to give SheepShaver another look.
SheepShaver is an open source project designed to emulate Power Mac hardware with versions for Mac OS X, Linux, Windows, and more. In order to make it work, you need to download a copy appropriate for your hardware and operating system, have handy a copy of the Mac operating system (versions 7.5.2 through 9.0.4 – and not a copy that’s tied to a specific piece of hardware), and access to a Mac ROM image. You need the ROM image in order to allow your emulated Mac to start the boot process – where standard Windows-style PCs have fairly simple ROM BIOSes, PowerPC Macs need access to a hunk of Apple-written (and Apple copyright) code before they start to load the operating system.
Catch-22
That Mac ROM image is the catch. If you have access to a PowerPC Mac from that late 1990s era, you could, presumably, make an image using the ROM Grabber utility. But you may want to emulate a PowerPC Mac because you don’t have access to an actual running computer of that era.
Alternatively, the firmware updater file included in the Mac OS 8.5 or 8.6 CD (in the System Folder) is supposed to be usable as a ROM image. It didn’t work for me – all I got was a black screen when I tried to start up SheepShaver. Apple has a Mac OS ROM Update available online that is also supposed to be usable in this way, but you need to be able to extract the ROM image from the software installer. The recommended way is to use a utility called TomeViewer. But TomeViewer is a Classic Mode program – if all you’ve got is an Intel Mac or a PowerPC Mac with Leopard (which is my situation), you can’t make it work. After all, running Classic Mode programs is what this is all about!
A hunt online got me a number of dead ends but eventually led me to a downloadable “New World PPC ROM”. I unzipped it, pointed SheepShaver to it, and was well on my way.
Setting Up SheepShaver
SheepShaver stores its critical settings in a text configuration file, but the Mac version includes a graphical front end that simplifies configuring it without having to ever touch a text editor. You’ll find it in your SheepShaver application folder, under the name SheepShaverGUI. It looks like an old Unix Motif-style application, rather than something designed for a Mac, but it’s pretty straightforward.
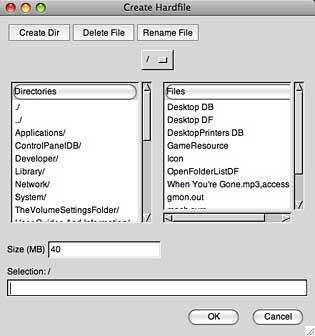 First, create a ‘volume’, a disk image, where you’ll be installing the classic Mac OS of your choice, by looking on the Volumes tab, and clicking the Create… button. I put mine in my Documents folder, so I scrolled down the Unix-style Directors list on the left to find Users, double-clicked to open it, found my name, opened it, scrolled down the list to find the Documents folder.
First, create a ‘volume’, a disk image, where you’ll be installing the classic Mac OS of your choice, by looking on the Volumes tab, and clicking the Create… button. I put mine in my Documents folder, so I scrolled down the Unix-style Directors list on the left to find Users, double-clicked to open it, found my name, opened it, scrolled down the list to find the Documents folder.
I gave it a size of 512 MB, and in the Selection box, gave it a name. When I clicked OK, nothing much seemed to happen for a moment or two, but after that, I had a 512 MB file with the proper name in my Documents folder.
Back to the Volumes settings tab. It showed my newly created virtual hard drive. The next setting, Unix Root, may seem obscure. In both Basilisk II and SheepShaver, when booted, the desktop shows at least two drive icons: one for the Mac boot drive, which we just created, and another one labeled Unix. Double-clicking it shows the contents of your ‘real’ Mac’s drive. With the root setting, you’re able to set how much of the Mac drive to make available – the default / makes the entire drive available; you might prefer to start with your Home folder (for instance, /Users/azisman in my case).
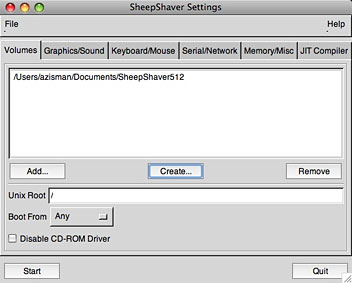 Next, you can set to boot from ‘Any’ or ‘CD-ROM’. If installing from a Mac OS CD, the latter might be the best choice – at least for your first boot. Finally, you have an option to disable the CD-ROM driver. We’ll see later that this might be a good choice for day-to-day operation.
Next, you can set to boot from ‘Any’ or ‘CD-ROM’. If installing from a Mac OS CD, the latter might be the best choice – at least for your first boot. Finally, you have an option to disable the CD-ROM driver. We’ll see later that this might be a good choice for day-to-day operation.
The Graphics/Sound tab lets you set the screen size; I picked 800 x 600. As well, you can enable or disable sound output. Sound works, but there may be a trick needed, which I’ll tell you about in a moment.
I didn’t need to do anything to the default settings on the Keyboard/Mouse tab. The Serial/Network tab is worth a quick peek – setting the Ethernet Interface option to ‘slirp’ let me get online using my Macs default networking setting – yes, it worked with both wired ethernet and an AirPort connection on the Mac.
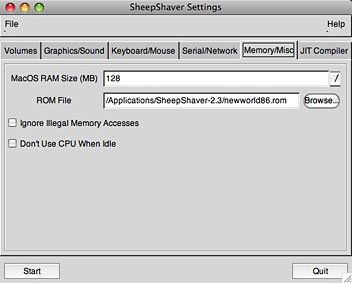 The Memory/Misc tab has two important settings. In the first, you need to set how much RAM to give your virtual Mac when it’s running. Your decision should depend on how much RAM is installed on your ‘real’ Mac; you don’t want to give the virtual Mac so much RAM that you starve OS X. But remember, Macs from that late 1990s-era didn’t have much RAM, at least by contemporary standards. I bought a G3 iMac in 1999, for instance, that came with either 32 or 64 MB (I forget – in either case, not very much). I gave my virtual Mac 128 MB; a large amount for a Mac of that era, but not so much that it will cause problems on my real Mac. (In any case, the real Mac gets the RAM back when SheepShaver isn’t running.)
The Memory/Misc tab has two important settings. In the first, you need to set how much RAM to give your virtual Mac when it’s running. Your decision should depend on how much RAM is installed on your ‘real’ Mac; you don’t want to give the virtual Mac so much RAM that you starve OS X. But remember, Macs from that late 1990s-era didn’t have much RAM, at least by contemporary standards. I bought a G3 iMac in 1999, for instance, that came with either 32 or 64 MB (I forget – in either case, not very much). I gave my virtual Mac 128 MB; a large amount for a Mac of that era, but not so much that it will cause problems on my real Mac. (In any case, the real Mac gets the RAM back when SheepShaver isn’t running.)
Finally, in that tab, you need to point to the location of your ROM image file. I copied mine into my SheepShaver application folder. I ignored the JIT Compiler folder.
When the SheepShaver GUI settings look okay, you can click its Start button in the lower-left corner. Alternatively, double-clicking the SheepShaver application file will just start it up, without giving you access to all those configuration settings.

Before starting SheepShaver for the first time, I inserted my OS 8.5 CD and set SheepShaver to boot from the CD. The CD installation program started up, but first it initialized my newly created virtual hard drive file, treating it just like a real Mac hard drive. Following that, I was able to install Mac OS 8.5 without problem, and (after resetting the configuration option to boot to ‘any’) was able to boot up to the ‘hard drive’ of my new 1998-era Mac.
I copied the SheepShaver application and virtual hard drive folder over from my PowerBook to my Intel iMac, so now I have two of them. Copying over was straightforward, though the copied-over ROM image didn’t work, so I downloaded another one.
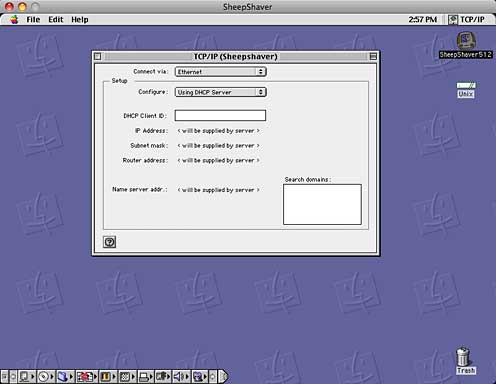
When starting up for the first time, Mac OS 8.5 tried to run a network setup routine. It seemed to be taking a long time to recognize the networking hardware, so I canceled it. After that, a little fiddling with the TCP/IP control panel was all it took to make Internet access happen. It seems happy just setting up for DHCP and leaving everything else blank.
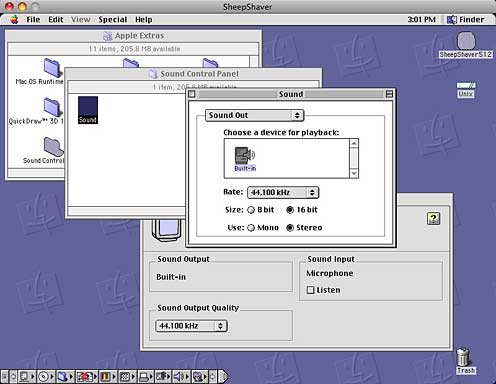
At first, there was no sound. It turns out that with Mac OS 8.5/8.6, the Monitors & Sound control panel isn’t the one you need to use – instead, look for the old Sound control panel, located in the \Apple Extras\Sound Control Panel folder; set Sound Out to Built-in, and you’re in business.
One more thing to avoid: OS 8.5/8.6 has a nice Appearance control panel. The Sound tab offers a ‘Platinum’ sound track. Choosing it immediately crashed my virtual Macs.
One more problem: CDs were accessible without problem, whether the CD was inserted into the Mac prior to starting SheepShaver or afterwards. But ejecting them was problematic. The ‘real’ Mac wouldn’t eject them, because they were still in use in SheepShaver. But ejecting them in SheepShaver just got me a spinning wheel. Better to shut down the virtual Mac, then eject the disc.
Inserting a USB memory stick did not get me an icon on my SheepShaver screen – but I could copy data from the memory stick to a location on my (real) Mac’s hard drive, then access that using the virtual Mac’s Unix drive icon.
Performance on my Intel iMac is pretty good, but performance on my older (PowerPC) 12″ PowerBook is spectacular – far and away the fastest classic Mac I’ve ever used. That’s because on an Intel Mac, SheepShaver has to emulate PowerPC instructions, translating them into Intel code; on a PowerPC Mac, no translation is necessary. As an example, it takes about 45 seconds to boot the virtual Mac on my 2 GHz Intel iMac. On my 1.5 GHz G4 PowerBook, the same thing takes 16 seconds. That makes it way faster than it used to take to start up Classic Mode!
Frankly, I don’t have much use for Classic Mode; I no longer depend on any of those older programs. But if you do, and you’re worried about not being able to run them after getting a new Mac or upgrading an older one to Leopard, SheepShaver may be your answer.
Or maybe it’s just fun to play with.
Keywords: #sheepshaver #macemulation #classicmacemulation
Short link: http://goo.gl/g1GWUe
searchword: sheepshaver